Due to the harsh working environment of the ship, the hull shell is subject to chemical corrosion of seawater, electrochemical corrosion and corrosion of marine organisms and microorganisms; the hull is subjected to large wind and wave impacts and alternating loads; the shape of the ship is complicated by processing methods, etc. Steel for hull structure is strictly required. First of all, good toughness is the most critical requirement. In addition, high strength, good corrosion resistance, weldability, forming properties and surface quality are required.
Shipbuilding Steels Our hot rolled shipbuilding steel is produced in accordance with the relevant Classification Society, examples of which include Lloyds Register and Det Norske Veritas.
Our steel products include steel shipbuilding plate, fabricated steel sections and floor plate for decking. We can also supply bulb flats for plate stiffening, structural steel angles and inverted angles.
Our plates are supplied under the ASTM/ASME specification (ASTM A131 / ASME SA 131) which is the standard specification for Structural Steel for Ships. We offer higher strength shipbuilding steels as standard .High strength steels offer significant cost advantages by reducing the weight of the structure in comparison to the steel used.
The plates are suitable for use in the construction of container ships and large cargo freighters as well as commercial shipping lines such as luxury cruise ships and ferries. Supply options include heavy plates, surface treated plates and pre-fabricated sections. In most cases, the steel can also be supplied as hot rolled coils or cut into lengths (sheets).
These high yield materials are commonly used in the construction of hulls and superstructures for large shipping vessels. The grades are exclusively for shipbuilding use as set out in the standard.
Ship Building Steel Plate,Shipbuilding Steel Plate,Marine Steel Plate,Shipbuilding Plate Shandong Guanzhou Iron and Steel Group Co., Ltd. , https://www.guanzhouiron.com
Vehicles with a current ratio higher than 1.5: GAC Group's highest Lifan upgrade
Of the 25 listed auto makers, the companies whose current ratio was above 2 at the end of 2009 and 2010 were only GAC Group. Its current ratio at the end of 2010 was 2.01, which was slightly lower than its level at the end of 2009 (2.03).
In addition to the GAC Group, there were four other companies with current ratios above 1.5 at the end of 2010, namely, Haima, Lifan, Jiangling, and FAW. Among them, the flow ratio of Lifan shares and Haima shares rose the fastest (at the same time, the statistical ratio of the fastest rising among the 25 companies), from 1.13 and 1.39 at the end of 2009 to 1.78 and 1.87 respectively.
Among the five companies mentioned above, except for Jiangling Motors' main business involving light commercial vehicles, the other four companies are mainly passenger car companies. 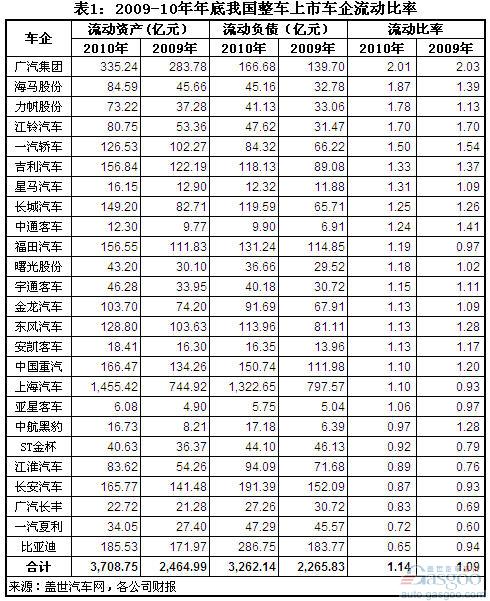
Car companies with current ratios ranging from 1 to 1.5: The fastest rising of Xingma car The fastest decline of Zhongtong bus
About half of the 25 car companies have a current ratio of between 1 and 1.5. At the end of 2009 and 2010, 13 companies (both passenger car companies and card and bus companies) had current ratios in this range. Among them, the current ratios of Geely Automobile, Great Wall Motors and Zhongtong Bus are both above 1.2.
At the end of 2010, the flow ratio of Xingma Automobile and Foton Motor Co., Ltd. rose the fastest among automakers with current ratios ranging from 1 to 1.5, from 1.09 and 0.97 at the end of 2009 to 1.31 and 1.19 at the end of 2010; followed by Shanghai Automotive. The 0.93 at the end of 2009 rose to 1.10 at the end of 2010. The fastest decline in the current ratio was Zhongtong Bus and Dongfeng Motor, which fell from 1.41 and 1.28 at the end of 2009 to 1.24 and 1.13 at the end of 2010 respectively.
Vehicles with current ratio below 1: BYD's lowest AVN Panther's decline is fastest. In general, the current ratio is not less than 1, which is the bottom line of the company's risk tolerance. Of the 25 vehicle companies listed in the statistics, 7 companies had a current ratio of less than 1 at the end of 2010, namely CNAF Panthers, ST Gold Cup, Jianghuai Automobile, Changan Automobile, GAC Changfeng, FAW Xiali and BYD. Among them, BYD has the lowest liquidity ratio, at 0.65, which is lower than its level at the end of 2009 (0.94).
At the end of 2009, the lowest flow rate among the 25 auto companies was FAW Xiali, which had a liquidity ratio of only 0.60. At the end of 2010, its current ratio rose to 0.72.
The AVIC Panthers’s current ratio fell the fastest (the fastest decline among the 25 companies surveyed), and the current ratio slipped from 1.28 at the end of 2009 to 0.97 at the end of 2010.
Ranking of China's Listed Vehicles' Current Ratio in 2010
The current ratio is used to measure the ability of corporate liquid assets to become cash for repaying liabilities before the short-term debt expires. Generally, the higher the ratio of the current ratio ratio, the stronger the short-term solvency of the company; The lower the current ratio, the weaker the company's short-term solvency. As an important indicator of the financial situation, it should be maintained at an appropriate level. Traditional wisdom holds that a current ratio of 2 is appropriate. According to Gasgoo.com's data on the number of vehicles listed by China's 25 automakers, the average current ratio of listed auto makers at the end of 2010 was 1.14, which is lower than the conventional value. Let's take a look at the specific flow rate of each car company.